Studies of Cellular Metabolism
Oxygen consumption and acid release
3.6.8.
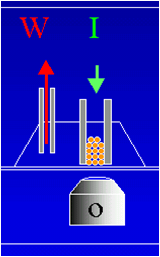
In this work, oxygen sensing was based on oxygen-dependent quenching of the phosphorescence of a Pt-porphyrin complex immobilized on microcarrier beads, which are used as the cell culture substrate. The changes of phosphorescence intensity were monitored by a modified fluorescence microscope equipped with a photomultiplier. Cellular respiration of Chinese Hamster Ovary M1 cells grown on Cytodex-3 microcarrier beads was monitored through O2 consumption measured
during a period of 3 min. The method was validated by detecting the impairment of aerobic metabolism caused by perfusing the cellular culture with 1.5 mM amobarbital. The method was found to be suitable to monitor even more subtle changes, such as the increase in oxygen consumption, caused by stimulation of the muscarinic m1 receptor with 100 íM carbachol.
The paper reviews the pathways in energy metabolism, and focuses on acid release and oxygen consumption, as parameters suitable for monitoring, BIS methods for monitoring of extracellular oxygen and pH changes by means of suitable indicators immobilized on bead surfaces. Along with discussion of a technique for monitoring of intracellular pH changes, measured by means of a pH indicator loaded into the cells, fluorescence microscopy and the SI-LOV technique served as experimental platforms.